One downside with Configuration Manager 2012 compared to Configuration Manager 2007 is that applications deployed to users, only made available, will not give a notification on the endpoint. This caused some initial confusion that needed a blog-post to clarify the matter – as all admins were used to a single view on the client what could be installed.
Microsoft created the Application Catalog, and for newer devices (mobile and Windows 8+) they made a secondary interface called the Company Portal (read about deployment at Justin Chalfants blog). However, none of these give a notification to the end user if an application is only made available.
Therefore I created a script in PowerShell that can just do that – ping the Application Catalog – check if there are new apps, and if so notify the user.
How does it work?
A scheduled task is setup

It starts the application 15 minutes after logon (to avoid excessive workload..), and then runs every 15 minutes.
After that, the workflow is something like;
Connect to Application Catalog
- If no previous check is completed, gather a list.No notification is given.
- If a previous check is completed, compare it.
- No difference? Do nothing
- New applications available? Notify the user
- Maintain a notification in the system tray (which directs the user to the Application Catalog if clicked)
- Applications removed? Update the list, no notification to the end-user
For each check there is a log file within the users %TEMP% called appsnotify app.log. Sample output;
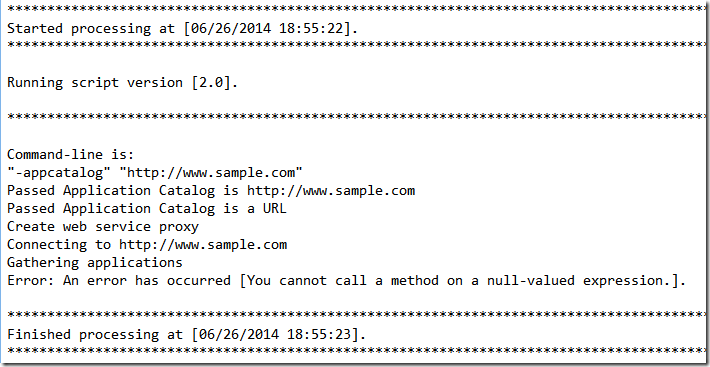
How does it look?
Like this;
How do I deploy it?
MSI-file to install it
To install it use the MSI file with the property APPCATALOG. Input should be;
APPCATALOG=http://localhost/CMApplicationCatalog
(no slash at the end)
The Application Catalog needs to be prepared for client interaction which is described by Microsoft in a blog-article. See the Getting Started section of Extending the Application Catalog in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager.
How do I make it my own?
In all Community spirit, here comes the code / files.
XML-file for creating the scheduled task – incase you want to build your own
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?>
<Task version="1.2" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2004/02/mit/task">
<RegistrationInfo>
<Author>PRECISION\Nicke</Author>
</RegistrationInfo>
<Triggers>
<LogonTrigger>
<Repetition>
<Interval>PT15M</Interval>
<StopAtDurationEnd>false</StopAtDurationEnd>
</Repetition>
<StartBoundary>1899-12-30T06:04:14</StartBoundary>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<Delay>PT15M</Delay>
</LogonTrigger>
</Triggers>
<Principals>
<Principal id="Author">
<GroupId>S-1-5-32-545</GroupId>
<RunLevel>LeastPrivilege</RunLevel>
</Principal>
</Principals>
<Settings>
<MultipleInstancesPolicy>IgnoreNew</MultipleInstancesPolicy>
<DisallowStartIfOnBatteries>false</DisallowStartIfOnBatteries>
<StopIfGoingOnBatteries>false</StopIfGoingOnBatteries>
<AllowHardTerminate>false</AllowHardTerminate>
<StartWhenAvailable>true</StartWhenAvailable>
<RunOnlyIfNetworkAvailable>true</RunOnlyIfNetworkAvailable>
<IdleSettings>
<StopOnIdleEnd>true</StopOnIdleEnd>
<RestartOnIdle>false</RestartOnIdle>
</IdleSettings>
<AllowStartOnDemand>true</AllowStartOnDemand>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<Hidden>true</Hidden>
<RunOnlyIfIdle>false</RunOnlyIfIdle>
<WakeToRun>false</WakeToRun>
<ExecutionTimeLimit>PT0S</ExecutionTimeLimit>
<Priority>7</Priority>
</Settings>
<Actions Context="Author">
<Exec>
<Command>C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\AppsNotify\AppsNotify 2.0.exe</Command>
<Arguments>-appcatalog http://www.sample.com</Arguments>
</Exec>
</Actions>
</Task>
Source code for the PowerShell script. Wrapped it into a .exe with PowerShell Studio 2012. I have only tested this on Windows 7 x64 with PowerShell 3.0 / 2.0. Log-functions are from 9to5it
#========================================================================
# Created on: 2014-06-10
# Created by: Nicke Källén
# Organization:
# Filename: AppsNotify 2.0.pff
#========================================================================
$AppNotify.FormBorderStyle = 'FixedToolWindow'
Function Log-Start{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Creates log file
.DESCRIPTION
Creates log file with path and name that is passed. Checks if log file exists, and if it does deletes it and creates a new one.
Once created, writes initial logging data
.PARAMETER LogPath
Mandatory. Path of where log is to be created. Example: C:\Windows\Temp
.PARAMETER LogName
Mandatory. Name of log file to be created. Example: Test_Script.log
.PARAMETER ScriptVersion
Mandatory. Version of the running script which will be written in the log. Example: 1.5
.INPUTS
Parameters above
.OUTPUTS
Log file created
.NOTES
Version: 1.0
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 10/05/12
Purpose/Change: Initial function development
Version: 1.1
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 19/05/12
Purpose/Change: Added debug mode support
.EXAMPLE
Log-Start -LogPath "C:\Windows\Temp" -LogName "Test_Script.log" -ScriptVersion "1.5"
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LogPath, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LogName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ScriptVersion)
Process{
$sFullPath = $LogPath + "\" + $LogName
#Check if file exists and delete if it does
If((Test-Path -Path $sFullPath)){
Remove-Item -Path $sFullPath -Force
}
#Create file and start logging
New-Item -Path $LogPath -Name $LogName –ItemType File
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value "***************************************************************************************************"
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value "Started processing at [$([DateTime]::Now)]."
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value "***************************************************************************************************"
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value ""
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value "Running script version [$ScriptVersion]."
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value ""
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value "***************************************************************************************************"
Add-Content -Path $sFullPath -Value ""
#Write to screen for debug mode
Write-Debug "***************************************************************************************************"
Write-Debug "Started processing at [$([DateTime]::Now)]."
Write-Debug "***************************************************************************************************"
Write-Debug ""
Write-Debug "Running script version [$ScriptVersion]."
Write-Debug ""
Write-Debug "***************************************************************************************************"
Write-Debug ""
}
}
Function Log-Write{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Writes to a log file
.DESCRIPTION
Appends a new line to the end of the specified log file
.PARAMETER LogPath
Mandatory. Full path of the log file you want to write to. Example: C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log
.PARAMETER LineValue
Mandatory. The string that you want to write to the log
.INPUTS
Parameters above
.OUTPUTS
None
.NOTES
Version: 1.0
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 10/05/12
Purpose/Change: Initial function development
Version: 1.1
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 19/05/12
Purpose/Change: Added debug mode support
.EXAMPLE
Log-Write -LogPath "C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log" -LineValue "This is a new line which I am appending to the end of the log file."
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LogPath, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LineValue)
Process{
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value $LineValue
#Write to screen for debug mode
Write-Debug $LineValue
}
}
Function Log-Error{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Writes an error to a log file
.DESCRIPTION
Writes the passed error to a new line at the end of the specified log file
.PARAMETER LogPath
Mandatory. Full path of the log file you want to write to. Example: C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log
.PARAMETER ErrorDesc
Mandatory. The description of the error you want to pass (use $_.Exception)
.PARAMETER ExitGracefully
Mandatory. Boolean. If set to True, runs Log-Finish and then exits script
.INPUTS
Parameters above
.OUTPUTS
None
.NOTES
Version: 1.0
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 10/05/12
Purpose/Change: Initial function development
Version: 1.1
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 19/05/12
Purpose/Change: Added debug mode support. Added -ExitGracefully parameter functionality
.EXAMPLE
Log-Error -LogPath "C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log" -ErrorDesc $_.Exception -ExitGracefully $True
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LogPath, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ErrorDesc, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][boolean]$ExitGracefully)
Process{
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value "Error: An error has occurred [$ErrorDesc]."
#Write to screen for debug mode
Write-Debug "Error: An error has occurred [$ErrorDesc]."
#If $ExitGracefully = True then run Log-Finish and exit script
If ($ExitGracefully -eq $True){
Log-Finish -LogPath $LogPath
Break
}
}
}
Function Log-Finish{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Write closing logging data & exit
.DESCRIPTION
Writes finishing logging data to specified log and then exits the calling script
.PARAMETER LogPath
Mandatory. Full path of the log file you want to write finishing data to. Example: C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log
.PARAMETER NoExit
Optional. If this is set to True, then the function will not exit the calling script, so that further execution can occur
.INPUTS
Parameters above
.OUTPUTS
None
.NOTES
Version: 1.0
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 10/05/12
Purpose/Change: Initial function development
Version: 1.1
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 19/05/12
Purpose/Change: Added debug mode support
Version: 1.2
Author: Luca Sturlese
Creation Date: 01/08/12
Purpose/Change: Added option to not exit calling script if required (via optional parameter)
.EXAMPLE
Log-Finish -LogPath "C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log"
.EXAMPLE
Log-Finish -LogPath "C:\Windows\Temp\Test_Script.log" -NoExit $True
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$LogPath, [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][string]$NoExit)
Process{
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value ""
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value "***************************************************************************************************"
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value "Finished processing at [$([DateTime]::Now)]."
Add-Content -Path $LogPath -Value "***************************************************************************************************"
#Write to screen for debug mode
Write-Debug ""
Write-Debug "***************************************************************************************************"
Write-Debug "Finished processing at [$([DateTime]::Now)]."
Write-Debug "***************************************************************************************************"
#Exit calling script if NoExit has not been specified or is set to False
If(!($NoExit) -or ($NoExit -eq $False)){
Exit
}
}
}
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
if($hostinvocation -ne $null)
{
Split-Path $hostinvocation.MyCommand.path
}
else
{
Split-Path $script:MyInvocation.MyCommand.Path
}
}
function Parse-Commandline
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Parses the Commandline of a package executable
.DESCRIPTION
Parses the Commandline of a package executable
.PARAMETER Commandline
The Commandline of the package executable
.EXAMPLE
$arguments = Parse-Commandline -Commandline $Commandline
.INPUTS
System.String
.OUTPUTS
System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection
#>
[OutputType([System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection])]
Param([string]$CommandLine)
$Arguments = New-Object System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection
if($CommandLine)
{
#Find First Quote
$index = $CommandLine.IndexOf('"')
while ( $index -ne -1)
{#Continue as along as we find a quote
#Find Closing Quote
$closeIndex = $CommandLine.IndexOf('"',$index + 1)
if($closeIndex -eq -1)
{
break #Can’t find a match
}
$value = $CommandLine.Substring($index + 1,$closeIndex – ($index + 1))
[void]$Arguments.Add($value)
$index = $closeIndex
#Find First Quote
$index = $CommandLine.IndexOf('"',$index + 1)
}
}
return $Arguments
}
function Convert-CommandLineToDictionary
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Parses and converts the commandline of a packaged executable into a Dictionary
.DESCRIPTION
Parses and converts the commandline of a packaged executable into a Dictionary
.PARAMETER Dictionary
The Dictionary to load the value pairs into.
.PARAMETER CommandLine
The commandline of the package executable
.PARAMETER ParamIndicator
The character used to indicate what is a parameter.
.EXAMPLE
$Dictionary = New-Object System.Collections.Specialized.StringDictionary
Convert-CommandLineToDictionary -Dictionary $Dictionary -CommandLine $Commandline -ParamIndicator '-'
#>
Param( [ValidateNotNull()]
[System.Collections.Specialized.StringDictionary]$Dictionary,
[string]$CommandLine,
[char] $ParamIndicator)
$Params = Parse-Commandline $CommandLine
for($index = 0; $index -lt $Params.Count; $index++)
{
[string]$param = $Params[$index]
#Clear the values
$key = ""
$value = ""
if($param.StartsWith($ParamIndicator))
{
#Remove the indicator
$key = $param.Remove(0,1)
if($index + 1 -lt $Params.Count)
{
#Check if the next Argument is a parameter
[string]$param = $Params[$index + 1]
if($param.StartsWith($ParamIndicator) -ne $true )
{
#If it isn’t a parameter then set it as the value
$value = $param
$index++
}
}
$Dictionary[$key] = $value
}#else skip
}
}
function Validate-IsURL
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Validates if input is an URL
.DESCRIPTION
Validates if input is an URL
.PARAMETER Url
A string containing an URL address
.INPUTS
System.String
.OUTPUTS
System.Boolean
#>
[OutputType([Boolean])]
param ([string]$Url)
if($Url -eq $null)
{
return $false
}
return $Url -match "^(ht|f)tp(s?)\:\/\/[0-9a-zA-Z]([-.\w]*[0-9a-zA-Z])*(:(0-9)*)*(\/?)([a-zA-Z0-9\-\.\?\,\'\/\\\+&amp;%\$#_]*)?$"
}
function Get-CMUserApps {
[CmdletBinding()]
param
(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='URL for Application Catalogue')]
$url,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='Path to logfile')]
$logfile,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='Temp-file')]
$temp
)
Begin {
log-write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Create web service proxy"
$catalogurl = $url;
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Connecting to $catalogurl"
try {
$url = $catalogurl+"/ApplicationViewService.asmx?WSDL";
$service = New-WebServiceProxy $url -UseDefaultCredential;
}
catch {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "AppCatalog no response" -ExitGraceFully $false
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $true
break
}
}
Process {
$total = 0;
try {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Gathering applications"
$service.GetApplications("Name",$null,"Name","",100,0,$true,"PackageProgramName",$false,$null,[ref]$total) | select ApplicationId,Name | Export-Clixml $temp
return $true
}
catch {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc $error[0] -ExitGraceFully $false
return $false
}
Remove-Variable -Name url
Remove-Variable -Name total
$service.dispose()
}
}
function Compare-CMUserApps {
[CmdletBinding()]
param
(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='Permanent-file')]
$file,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='Temp-file')]
$temp,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True,
HelpMessage='Path to logfile')]
$logfile
)
Process {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Comparing applications lists"
If (-Not (Test-Path $file)) {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "No previous version of apps list"
try {
Rename-Item $temp "$prefix apps.xml"
}
catch {
Remove-Item $temp
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to create initial list" -ExitGracefully $false
}
}
Else {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Starting check......"
# $diffs = (Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $(Get-Content $file) -DifferenceObject $(Get-Content $temp)) | Where {$_.SideIndicator -eq '<='}
# $diffsserver = (Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $(Get-Content $file) -DifferenceObject $(Get-Content $temp)) | Where {$_.SideIndicator -eq '=>'}
If ((Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $(Get-Content $file -ReadCount 0) -DifferenceObject $(Get-Content $temp -ReadCount 0)) -eq $null) {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "No new applications"
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Removing temporary file"
try {
Remove-Item $temp
}
catch {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to remove temp list" -ExitGracefully $false
}
}
Elseif (((Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $(Get-Content $file -ReadCount 0) -DifferenceObject $(Get-Content $temp -ReadCount 0)) | Where {$_.SideIndicator -eq '<='}) -ne $null -and ((Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $(Get-Content $file -ReadCount 0) -DifferenceObject $(Get-Content $temp -ReadCount 0)) | Where {$_.SideIndicator -eq '=>'}) -eq $null ) {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Less applications received"
try {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Remove permanent list"
Remove-Item $file
}
catch {
Remove-Item $temp
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to remove permanent list" -ExitGracefully $false
}
try {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "Rename temporary list"
Rename-Item $temp "$prefix apps.xml"
}
catch {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to switch temp-list to permanent" -ExitGracefully $false
}
}
Else {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfile -LineValue "New applications found"
$newapps = $true
}
}
If ($newapps -eq $true) {
return $True
}
}
}
function OnApplicationLoad {
#Note: This function is not called in Projects
#Note: This function runs before the form is created
#Note: To get the script directory in the Packager use: Split-Path $hostinvocation.MyCommand.path
#Note: To get the console output in the Packager (Windows Mode) use: $ConsoleOutput (Type: System.Collections.ArrayList)
#Important: Form controls cannot be accessed in this function
#TODO: Add snapins and custom code to validate the application load
return $true #return true for success or false for failure
}
function OnApplicationExit {
#Note: This function is not called in Projects
#Note: This function runs after the form is closed
#TODO: Add custom code to clean up and unload snapins when the application exits
#Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $true
$script:ExitCode = 0 #Set the exit code for the Packager
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
$AppNotify_Load={
#TODO: Initialize Form Controls here
$NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip(30000,"New Application","You have new applications available", 'Info')
}
#region Control Helper Functions
function Show-NotifyIcon
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Displays a NotifyIcon's balloon tip message in the taskbar's notification area.
.DESCRIPTION
Displays a NotifyIcon's a balloon tip message in the taskbar's notification area.
.PARAMETER NotifyIcon
The NotifyIcon control that will be displayed.
.PARAMETER BalloonTipText
Sets the text to display in the balloon tip.
.PARAMETER BalloonTipTitle
Sets the Title to display in the balloon tip.
.PARAMETER BalloonTipIcon
The icon to display in the ballon tip.
.PARAMETER Timeout
The time the ToolTip Balloon will remain visible in milliseconds.
Default: 0 - Uses windows default.
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, Position = 0)]
[ValidateNotNull()]
[System.Windows.Forms.NotifyIcon]$NotifyIcon,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, Position = 1)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[String]$BalloonTipText,
[Parameter(Position = 2)]
[String]$BalloonTipTitle = '',
[Parameter(Position = 3)]
[System.Windows.Forms.ToolTipIcon]$BalloonTipIcon = 'None',
[Parameter(Position = 4)]
[int]$Timeout = 0
)
if($NotifyIcon.Icon -eq $null)
{
#Set a Default Icon otherwise the balloon will not show
$NotifyIcon.Icon = [System.Drawing.Icon]::ExtractAssociatedIcon([System.Windows.Forms.Application]::ExecutablePath)
}
$NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip($Timeout, $BalloonTipTitle, $BalloonTipText, $BalloonTipIcon)
}
#endregion
$NotifyIcon_MouseDoubleClick=[System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler]{
#Event Argument: $_ = [System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs]
#TODO: Place custom script here
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "User clicked icon"
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Sending user to $appcatalog"
Start-Process $appcatalog
$NotifyIcon.Visible = $false
try {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Removing $filepath"
Remove-Item $filePath
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Renaming $tempfilePath"
Rename-Item -Path "$tempfilePath" -NewName "$prefix apps.xml" -Force
}
catch {
Remove-Item $tempfilePath
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to remove permanent list" -ExitGracefully $false
}
$AppNotify.Close()
$NotifyIcon.Dispose()
#Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
#$AppNotify.Close()
#$timer1.Start()
}
$NotifyIcon_MouseClick=[System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler]{
#Event Argument: $_ = [System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs]
$NotifyIcon.Visible = $true
$NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip(30000,"New Application","You have new applications available", 'Info')
}
$NotifyIcon_BalloonTipClicked={
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "User clicked ballontip"
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Sending user to $appcatalog"
Start-Process $appcatalog
$NotifyIcon.Visible = $false
try {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Removing $filepath"
Remove-Item $filePath
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Renaming $tempfilePath"
Rename-Item -Path "$tempfilePath" -NewName "$prefix apps.xml" -Force
}
catch {
Remove-Item $tempfilePath
Log-Error -LogPath $logfile -ErrorDesc "Unable to remove permanent list" -ExitGracefully $false
}
$AppNotify.Close()
$NotifyIcon.Dispose()
#Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $true
#exit
#$timer1.Start()
}
#Get path which scripts run from
$CurrentPath = Get-ScriptDirectory
#Prefix for all generated files in user's %TEMP%
$prefix = "appsnotify"
#Logfile
$logfilePath = $env:temp+"\$prefix app.log"
$check=Get-Process AppsNotify -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Measure-Object
if ($check.count -lt "2") {
}
else {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfilePath -ErrorDesc "AppsNotify is already running. Terminating. " -ExitGraceFully $false
exit
}
#Temporary file to store applications
$tempfilePath = $env:temp+"\$prefix app_temp.xml"
#Permanent file to store applications
$filePath = $env:temp +"\$prefix apps.xml"
#Reset log-file for this session
Remove-Item $logfilePath
################################################################################################################
Log-Start -LogPath $env:temp -LogName "$prefix app.log" -ScriptVersion "2.0"
#Verify that the $CommandLine variable exists
if($CommandLine -ne $null -and $CommandLine -ne "")
{
#Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "There is a command-line"
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Command-line is:"
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "$CommandLine"
#$Arguments = Parse-Commandline $CommandLine
#Convert the Arguments. Use – as the Argument Indicator
$Dictionary = New-Object System.Collections.Specialized.StringDictionary
Convert-CommandLineToDictionary -Dictionary $Dictionary -CommandLine $Commandline -ParamIndicator '-'
}
else
{
#Not running in a packager or no command line arguments passed
Log-Error -LogPath $logfilePath -ErrorDesc "No command-line argument. Use -appcatalog <url>" -ExitGraceFully $false
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
$appcatalog = $Dictionary["appcatalog"]
if($appcatalog -ne $null -and $appcatalog -ne "") {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Passed Application Catalog is $appcatalog"
if (Validate-IsURL -Url $appcatalog) {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Passed Application Catalog is a URL"
}
Else {
Log-Error -LogPath $logfilePath -ErrorDesc "This is not a url" -ExitGraceFully $false
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
}
else {
#Address to Application Catalogue
Log-Error -LogPath $logfilePath -ErrorDesc "We need an Application Catalog" -ExitGraceFully $false
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
if ((Get-CMUserApps -url $appcatalog -logfile $logfilePath -temp $tempfilePath) -eq $true) {
if ((Compare-CMUserApps -file $filePath -temp $tempfilePath -logfile $logfilePath) -eq $true) {
try {
$NotifyIcon.Visible = $true
}
catch {
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Exception"
}
$NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip(30000,"New Application","You have new applications available", 'Info')
}
Else {
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
}
Else {
Log-Finish -LogPath $logfilePath -NoExit $false
break
}
$NotifyIcon_BalloonTipShown={
#TODO: Place custom script here
Log-Write -LogPath $logfilePath -LineValue "Notifying user"
}
}